Recently someone asked me what is the best way to filter on a multi-valued columns in Power BI.
The question was in the context of Tags property of the Work Items - Today table in the Visual Studio Team Services [1].
Although the original question was very specific, the solution I came up with can be generalized to multivalued columns in any data model.
What is a multivalued column?
Multivalued column is a database design pattern where instead of normalizing and splitting data across multiple tables you keep multiple values in a single table.
You can see it typically in the data warehouses where normalization would lead to a too granular fact tables.
One of the best examples is the Categories column in the Product table where want to allow users to select multiple values, but you don't want to create a separate Categories table.
In the context of Visual Studio Team Services there is one table where this pattern was applied - Work Items - Today.
It contains Tags column which is a "; " delimited list of tags like in the example below.
| Work Item Id | Title | Tags |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add column A to table B | database; milestone1 |
| 2 | Create migration script | database |
| 3 | Improve performance of slow queries | performance; database |
| ... | ... | ... |
Problem statement
Given table with a multivalued column prepare data model that will allow users to easily filter on distinct values.
For example, we can start with the table below, which has multivalued Tags column.
let
Source = #table(
{"Work Item Id", "Title", "Tags"},
{
{ "1", "Add column A to table B", "database; milestone1" },
{ "2", "Create migration script", "database" },
{ "3", "Improve performance of slow queries", "performance; database" }
})
in
Source
If we simply selected Tags for the slicer it would produce the following result.
Instead of values users could only select combinations that appear in the dataset.
That's not what we want.
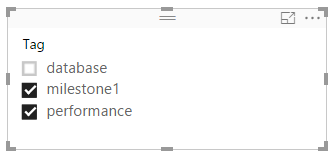
A much better design is to extract distinct values from the Tags column so that we can build the following slicer.
Solution
The solution I would like to show you is based on the post by SQLJason where he talks about handling delimited rows [2]. I modernized and improved it a little to cover columns of arbitrary length and to avoid contaminating model with auxiliary tables. The idea stays the same and can be broken down into the following steps.
- Create temporary index table.
- Apply
CROSSJOINoperation and convert source table from wide to long format. - Define relationships.
In my previous post "Creating index table in DAX" I explained how to create index table for a given N. Here, N should be selected as the max number of elements in the multivalued column.
MaxLength =
VAR Separator = "; "
RETURN
MAXX (
'Work Items - Today',
1 + LEN ( [Tags] )
- LEN ( SUBSTITUTE ( [Tags], Separator, "" ) )
)
Now we can use this DAX expression and create Indexes table.
Indexes =
VAR Separator = "; "
RETURN
FILTER (
SUMMARIZE (
ADDCOLUMNS (
CALENDAR (
DATE ( 2000, 1, 1 ),
DATE ( 2000
+ MAXX (
'Work Items - Today',
1 + LEN ( [Tags] )
- LEN ( SUBSTITUTE ( [Tags], Separator, "" ) )
), 1, 1 )
),
"Index", YEAR ( [Date] ) - 2000
),
[Index]
),
[Index] > 0
)
| Index |
|---|
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
We do not need to store this table in our model. Instead, we can simply save it in the DAX variable and reuse later.
The final expression consists of the following operations:
- Save separator in the variable.
- Create index table.
- Add
TagsCountto theWork Item - Todaytable to keep track of the index range. - Apply
CROSSJOINwithIndexestable. - Filter out indexes that are outside of the range.
- Use
PATHITEMto extract single value from the multivalued field by index and save it inTagcolumn. - Summarize to reduce set of columns in the output table.
Tags =
VAR Separator = "; "
VAR Indexes =
FILTER (
SUMMARIZE (
ADDCOLUMNS (
CALENDAR (
DATE ( 2000, 1, 1 ),
DATE ( 2000
+ MAXX (
'Work Items - Today',
1 + LEN ( [Tags] )
- LEN ( SUBSTITUTE ( [Tags], Separator, "" ) )
), 1, 1 )
),
"Index", YEAR ( [Date] ) - 2000
),
[Index]
),
[Index] > 0
)
RETURN
SUMMARIZE (
ADDCOLUMNS (
FILTER (
CROSSJOIN (
ADDCOLUMNS (
'Work Items - Today',
"TagsCount", 1
+ ( LEN ( [Tags] ) - LEN ( SUBSTITUTE ( [Tags], Separator, "" ) ) )
/ LEN ( Separator )
),
Indexes
),
[Index] <= [TagsCount]
),
"Tag", PATHITEM ( SUBSTITUTE ( [Tags], Separator, "|" ), [Index] )
),
[Work Item Id],
[Tag]
)
It will produce the following result. This table captures relationship between work items and tags.
| Work Item Id | Tag |
|---|---|
| 1 | database |
| 2 | database |
| 3 | performance |
| 1 | milestone1 |
| 3 | database |
Now we need to define relationships and specify cross filtering direction. First, task is easy because most likely Power BI will automatically detect the relationship like in the example below.
The automatic relationship is a standard one-to-many relationship, which means that it will allow us to filter Tags based on Work Item - Taday selection.
That is exactly opposite of what we need.
Double-click on the relationship to open the advanced editor and under "Cross filter direction" select "Both".
Finally, create a new slicer with Tag field from the newly created Tags table to get the best filtering experience! You can also try out amazing Smart Filter custom visual, which fits perfectly for this scenario.
References:
- Team Services & TFS - Available data tables in the Power BI Data Connector for Team Services
- Split a Delimited Row into Multiple Rows using DAX Queries
- It is not overengineering - Creating index table in DAX
- Custom visuals for Power BI - Smart Filter by OKViz
- SQLBI - Best Practices Using SUMMARIZE and ADDCOLUMNS
- Power BI Documentation - Calculated tables in Power BI Desktop




Brak komentarzy:
Prześlij komentarz